Recently updated on August 22nd, 2024 at 06:08 am
Zany: I’ve heard the excuses for incidences of antiblack police violence from members of my own family: “Black communities are dangerous.” “Black people commit the most crimes, so police have to be more suspicious and careful that a Black person could be a criminal.” Even when I share the obvious differences among people stopped by police depending on the race of the person driving, it doesn’t change the opinions that races are treated equally by police.
Young people have been shot and killed for fleeing from a traffic stop because they weren’t White. Meanwhile, a recent video showed an older White woman who was pulled over disrespecting the officer, attempting to drive off once, then doing it again successfully. What happened to her? She was mailed a ticket for the illegal U-turn that led to her being stopped in the first place. No charge for fleeing and evading?
It’s not crazy to say that if she wasn’t White, she wouldn’t have gotten away with refusing to give the officer her insurance card, disrespecting him, refusing to give him her keys after attempting to drive off, and then fleeing successfully. She would’ve had her car window broken, been drug out of the car and arrested, or possibly shot. At the very least, the officer would’ve jumped in his car and chased her. Once he caught up to her, she would’ve been “punished” for fleeing instead of having the charge determined by judge and jury.
Too many police officers act as prosecutors, judges, and juries. Some officers sentence the driver to the death penalty—and then proceed to carry it out. You can take any incident of police violence—or police shooting/killing—and replace the victim with a White person and the entire interaction with police will change drastically with no one being shot or killed. That reminds me of the White man in a pickup truck that police chased, an officer hung onto the hood of the truck as he drove, fleeing several times—and it ended with his arrest. He wasn’t shot through the windshield or the rear window after almost hitting the officer or fleeing for the 3rd time.
It’s been noted many times how Black men are shot and killed during a suspected criminal act while White males are arrested after committing a mass shooting when caught in the act by police. Yes, sometimes the mass shooter is shot and killed, but when that doesn’t happen, he is out in handcuffs without being slammed to the ground, punched, kicked, tased, choked, or shot.
How about the White woman who told police to “Shut the f*** up!” what would’ve happened if she was Black?

Antiblack police violence in America
A decade ago, Michael Brown Jr., an unarmed Black 18-year-old, was shot and killed by a white police officer in Ferguson, Missouri, a suburb of St. Louis.
The fatal incident began when the officer, Darren Wilson, saw Brown and a friend walking down the middle of a street. Wilson claimed that Brown refused to obey his order to get off the street and a fight ensued. The shooting, Wilson alleged, was in self-defense – a claim that officers have used nationwide to justify antiblack police violence.
Brown’s death on Aug. 9, 2014, occurred just eight days after his high school graduation and triggered nearly a year of protests across the country. Three months later, a grand jury in Ferguson refused to indict the police officer, a decision that set off more protests and demands for racial justice in policing.

Nearly 10 years later and less than 90 miles away from Ferguson, Sonya Massey, an unarmed, 36-year-old Black woman and mother of two children, called local police on July 6, 2024, to investigate mysterious sounds outside of her home near Springfield, Illinois.
Instead of helping, one of the white officers, Sean Grayson, shot and killed Massey. As her son Malachi told reporters, the officer showed little regard for her humanity during the slaying that was captured on body-camera footage. At the officer’s request, Massey had taken a pot of hot water from the stove. Minutes later, she was killed when Grayson fired three bullets, including one that hit right below her eye.
Unlike Brown’s case in Ferguson, Grayson was fired from the Sangamon County Sheriff’s Office and charged with first-degree murder. Similar to Darren Wilson, he claimed he acted in self-defense.
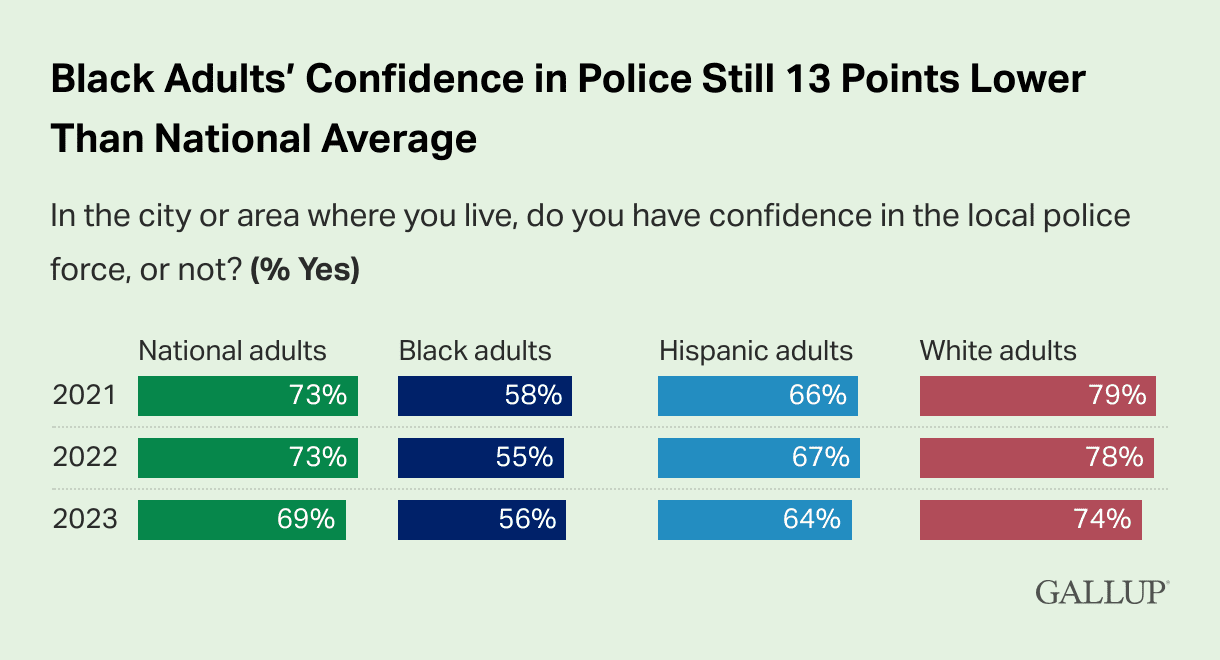
These two instances of Antiblack police violence highlight the cyclical nature of police violence against Black Americans – and the growing mistrust among Black Americans for local police.
From 2009-2019, at least 179 people have been killed by police or while in jail within four counties of the St. Louis region near where Brown died.
These local statistics mirror nationwide patterns of antiblack police violence in the U.S. and reveal that Massey and Brown were not exceptions to the norm – but, rather, representative of the everyday racism that pervades American society.
As we have learned through our research of racist violence in Black communities, developing ways to cope is often a necessary reality of living in the United States.
What is racial grief?
With every new incident of racial violence committed by a police officer, Black people tend to experience a collective sense of racial grief.
That grief is defined by the U.S. National Institutes of Health as an “individuals’ cognitive, emotional, physical, and spiritual responses to loss due to racism and intersectional violence.”
In addition, many Black parents experience a type of anticipatory grief and stress due to the potential racial violence their children may encounter in their lifetime.
For instance, in a 2022 study, researchers found Black pregnant women experienced feelings of fear, stress and anxiety about police brutality toward their children – before their children were born. Even mothers who reported positive experiences with police officers anticipated negative treatment toward their children based on their race.
Racial grief can represent a coping response that allows Black parents to emotionally and cognitively process incidents of antiblack police violence in community with others.
In our 2022 study, one mother told us:
“I can’t watch the videos anymore. It is a living nightmare, and I do not need those images, because they cannot be unseen. It takes a heavy toll on me. I cope with it in therapy. I cry. I give myself space to feel my feelings. I talk with my partner about it. It gives me a sense of pain and purpose at the same time.”
How do Black parents respond to police violence
When parents think about how they can prepare their children for the racial discrimination they may encounter in their daily lives, many use what is known as racial socialization to improve they and their children’s adaptive coping responses in response to racial bias and discrimination.

Racial socialization refers to the process by which parents instill race-related messages and values in their children. It is considered by psychologists to be one of the most critical developmental processes for Black youth and includes both implicit and explicit practices.
For instance, some parents monitor the content of their children’s social media and limit their exposure to racial violence. Other parents balance messages on racial discrimination with affirmations that their children are loved, worthy and valued.
Common racial socialization messages include statements such as: “You should be proud to be Black.” A message on racial bias might involve: “You may be evaluated by higher standards than your white peers.”
Overall, these messages are intended to elicit racial and cultural pride, while also encouraging Black youth to be cautious and aware of the ongoing realities of racial violence.
In a forthcoming study we have on how Black parents in Missouri talk to their adolescents about race, one mother shared:
“Like with the Sonya Massey thing, my daughter saw the video and she was like – ‘but she didn’t do anything wrong.’ That’s usually what happens. Like I told her, she called the police for help and they end up killing her. It happens sometimes because they act like they’re scared of Blacks for some reason. I feel like we are not progressing in America with this racism thing.”
While Black parents and their children continue to resist racial discrimination through their everyday practices of care, love and joy, there remains a critical need to invest in the health and well-being of Black communities through structural policy changes in education, health care and local government.
Seanna Leath receives funding from the National Science Foundation, Russell Sage Foundation, and the Society for Research on Child Development.
Sheretta T. Butler-Barnes receives funding from the National Science Foundation.
The article featured in this post is from The Conversation and republished here under a Creative Commons License. Read the original article.









