Climate change is one of the most important issues we face today, with far-reaching consequences that extend beyond environmental concerns—into the realm of politics, economics, and social justice. As the effects of climate change are becoming more obvious, governments around the world are grappling with how to respond effectively. This article explores how climate change influences political decisions, examines recent legislative developments, and looks at how public opinion and advocacy efforts affect policy. By analyzing these various parts of the process, we hope to understand how political landscapes are being transformed in response to the climate crisis.
The Connection Between Climate Change and Politics
Understanding Climate Change
At its core, climate change refers to significant changes in global temperatures and weather patterns over time. While climate change is a natural phenomenon, the current crisis is largely driven by human activities, particularly through the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation.
The increase in greenhouse gas emissions has led to rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and biodiversity loss. Understanding these scientific principles is crucial in making political decisions, as legislators must base their actions on credible scientific evidence and projections, not misinformation and conspiracy theories.
Climate change poses risks to public health, agriculture, and global security, so it requires a comprehensive approach to creating legislation. The complexity of the issue means there must be conversations that include science, economics, ethics, and social equity. Policymakers must weigh environmental sustainability against economic growth, creating a challenging but necessary balancing act in politics.
The Role of Government in Climate Action
Governments play a critical role in addressing climate change through legislation, regulation, and international agreements. They are responsible for setting emissions reduction targets, promoting renewable energy, and safeguarding natural resources. Through legislation, governments can incentivize businesses and individuals to adopt greener practices. This not only includes direct measures like carbon pricing but also indirect actions such as investing in public transportation and urban infrastructure that supports sustainable living.
Other countries, like Germany, have already transformed public transportation into electric options vs. the gas-powered buses still in use here in the U.S. Some U.S. cities have already begun using community-based solar power—a practice where panels are installed on the tallest building in the community and the residents all chip-in on the cost in exchange for use of the electricity that is generated. Rooftop gardens are another example of urban infrastructure using greener practices.

The effectiveness of governmental action on climate change often depends on the desire of politicians to react and public support for greener policies. Legislators have to navigate complex political landscapes, which can include opposition from various interest groups, like the fossil fuel industry. This requires a strategic approach in crafting legislation that is not focused on mitigating climate change but that also considers the socio-economic implications for their constituents.
Recent Legislative Developments
Major Climate Bills Passed
In recent years, several major climate bills have been passed at both state and federal levels, reflecting a growing acknowledgment of the urgency of climate action. The United States, for instance, has seen the introduction of ambitious legislation like the Green New Deal, which aims to address climate change while promoting social justice and job creation, though getting it passed seems like a faraway dream with the current members of Congress. Similarly, the Inflation Reduction Act emphasized investments in clean energy technologies, aiming to reduce greenhouse gas emissions significantly by 2030.
Internationally, agreements like the Paris Accord have galvanized collective action towards limiting the rise in global temperatures. Countries are increasingly committing to national targets that reflect their climate ambitions, demonstrating how international cooperation can influence domestic policy decisions. The passage of these legislative measures signals a shift in priorities, as governments respond to scientific data and public demand for immediate action. Young climate activists have been especially ambitious when it comes to pushing governments to take action.

Key Policies and Their Impacts
Key policies initiated through recent legislation have broad implications for both the environment and the economy. For instance, renewable energy tax credits incentivize investment in solar and wind energy, driving down costs and increasing adoption rates across the nation. Such initiatives have the potential to create thousands of jobs in green industries, thereby promoting economic growth while simultaneously addressing climate change.
Establishing stricter emissions standards for vehicles and industries can lead to significant reductions in air pollution, improving public health issues. The nexus of environmental policy and public health highlights the multiple benefits of climate legislation, which extend beyond ecological preservation to enhance the quality of life for humanity around the world.
Case Studies
State-Level Initiatives
While federal legislation often garners significant attention, many impactful climate initiatives are taking place at the state level. States like California have been pioneers in enacting progressive climate policies, such as the cap-and-trade program aimed at reducing carbon emissions from major polluters. These state-level efforts serve as critical examples of experimentation with different policy solutions, often influencing the national conversation.
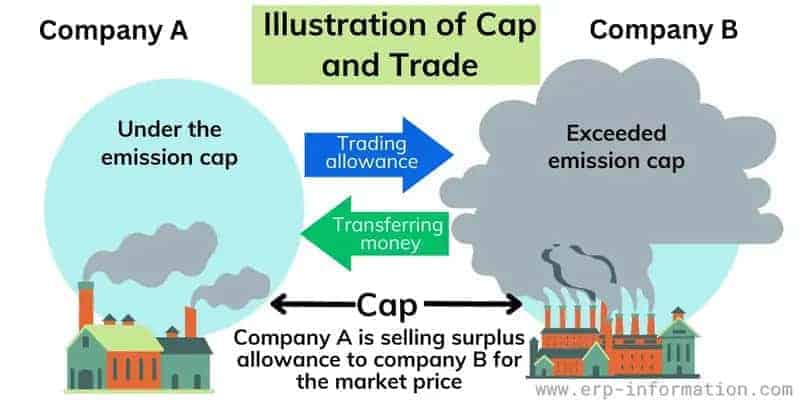
Local governments are more commonly adopting climate action plans that include strategies for sustainable urban development, waste reduction, and renewable energy initiatives. Such localized approaches allow for tailored strategies that address specific community needs, demonstrating that grassroots actions can complement national and international efforts in combating climate change.
Federal Legislation Examples
On the federal level, initiatives such as the Clean Power Plan represent efforts to reduce emissions from power plants and transition towards cleaner energy sources. Although challenges have arisen in implementation and opposition, these policies reflect a commitment to aligning governmental priorities with scientific recommendations for climate action. The significance of these federal efforts lies in their potential to set national standards that can shape state policies and corporate practices.
Federal investments in research and development of renewable technologies are important for fostering innovation and competitiveness in the global market. By prioritizing clean energy solutions, the government can stimulate economic growth while addressing climate challenges, and in doing so, enhance national security and environmental stability.
Political Parties and Climate Change
Democratic Approaches
The Democratic Party largely advocates for aggressive climate action and renewable energy investment. Their approach emphasizes the importance of government intervention to address environmental injustices and promote sustainability. Initiatives from Progressives, such as the Green New Deal encapsulate a vision for a comprehensive response to climate change that includes economic revival, social equity, and environmental protection.
Democrats often prioritize international cooperation on climate issues, seeking to re-engage with global agreements like the Paris Accord. Their commitment to building a greener economy is evident in proposed policies that not only aim to reduce emissions but also enhance job opportunities in renewable sectors, thereby aligning economic growth with environmental stewardship.
Republican Perspectives
In contrast, the Republican Party tends to adopt a more cautious approach to climate change, often emphasizing economic considerations over environmental regulations. Some members advocate for market-driven solutions rather than government-led initiatives, arguing that innovation in the private sector will yield more effective outcomes for reducing emissions and promoting sustainability.
This perspective can lead to significant policy divides, particularly concerning federal mandates and regulations versus state-led initiatives. While some Republican leaders have begun to acknowledge the importance of climate action, the party remains fragmented on how best to address these issues, with some members continuing to refer to climate change as a hoax, spreading misinformation that causes the public to see action as wasteful and non-essential.
Public Opinion and Advocacy
The Role of Activism in Legislation
Public opinion plays a crucial role in shaping political decisions related to climate change. Grassroots movements and environmental advocacy groups have been instrumental in raising awareness and mobilizing citizens to demand action. Events like climate strikes and advocacy campaigns have captured the attention of lawmakers and the media, creating pressure to prioritize climate issues in legislative agendas.
Additionally, high-profile youth activists and organizations have invigorated the climate movement, emphasizing the moral imperative to act on behalf of future generations. The increased visibility of climate issues in public discourse has prompted many legislators to rethink their positions and align themselves with constituents who advocate for urgent climate action.
How Public Sentiment Drives Political Action
Polling data consistently demonstrates a growing concern among the public regarding climate change, with many indicating a willingness to support policies that promote sustainability. This shift in public sentiment is particularly evident among younger voters, who prioritize environmental issues when casting their ballots. Political candidates are increasingly recognizing the electoral significance of addressing climate change, leading to a heightened focus on environmental platforms in campaigning.
Moreover, the intersection of social justice and climate change has sparked discussions about equity and inclusion in climate legislation. Advocacy for marginalized communities disproportionately affected by climate impacts has gained traction, reflecting an evolving understanding of environmental justice that resonates with a broad spectrum of the electorate.
Challenges in Climate Legislation
Political Polarization
Despite a growing consensus on the need for climate action, political polarization continues to pose substantial challenges to effective legislation. Divergent views on climate change, particularly between major political parties, can stall or dilute important policy initiatives. This polarization often leads to a lack of bipartisan support for critical measures, making it difficult to achieve comprehensive climate legislation that meets urgent needs.
The influence of corporate lobbying and special interest groups can further complicate the political landscape, as some sectors resist regulatory changes that could impact their profitability. Addressing climate change thus requires not only scientific and public support but also a concerted effort to bridge political divides and foster collaboration across party lines.
Economic Concerns and Trade-offs
Economic considerations are frequently cited as a reason for hesitancy in climate action. Many politicians express concerns over the potential costs of transitioning to a greener economy, arguing that it could lead to job losses in traditional industries such as coal and oil. This apprehension can hinder the adoption of effective climate policies, as lawmakers weigh short-term economic impacts against long-term environmental benefits.
The Future of Climate Legislation
Predictions for Upcoming Sessions
Looking ahead, the future of climate legislation remains uncertain, shaped by shifting political landscapes and public opinion. As climate impacts become increasingly severe and visible, it is likely that the urgency for comprehensive climate action will continue to grow. This may lead to new legislative opportunities, particularly if public demand for action continues to rise.
Moreover, advancements in technology and renewable energy may create pathways for bipartisan support in addressing climate challenges. As economic benefits become more apparent, there may be a shift in how climate policies are framed, focusing on the potential for innovation and job creation rather than purely on regulatory concerns.
Innovative Solutions on the Horizon
The upcoming years may also see the emergence of innovative solutions that combine technology, community engagement, and policy frameworks. Ideas such as carbon capture and storage, sustainable agriculture practices, and circular economy models are gaining traction as potential strategies to mitigate climate impacts. These innovations not only address environmental concerns but also present economic opportunities that can garner broader political support.
Ultimately, the intersection of science, public advocacy, and political action will determine the future trajectory of climate legislation. By fostering a collaborative environment that prioritizes sustainability, governments can forge a path towards a resilient and equitable future.
Reinforcing the Importance of Climate Awareness
The relationship between climate change and politics is complex. The urgency of climate issues has prompted significant legislative action, but challenges remain due to political polarization and economic concerns. Understanding this dynamic is crucial for fostering informed discussions and effective advocacy for climate action.

It is essential for citizens to remain engaged and hold their elected officials accountable to prioritize climate policies that protect the environment and promote social equity. The collective action of informed constituents can drive meaningful change and encourage policymakers to embrace innovative solutions that address the climate crisis.
FAQs
What is the Green New Deal? The Green New Deal is a proposed legislative framework aimed at addressing climate change and economic inequality in a coordinated effort. It seeks to transition to renewable energy sources while creating jobs and ensuring social justice.
How do state-level initiatives impact federal legislation? State-level initiatives can serve as models for federal policies, showcasing successful strategies and garnering public support for broader action. They can also push federal lawmakers to adopt more ambitious climate goals.
What role do advocacy groups play in climate legislation? Advocacy groups raise awareness, mobilize public opinion, and lobby lawmakers to prioritize climate action. They often serve as key stakeholders in the legislative process, ensuring that diverse voices are heard.
Why is political polarization a barrier to climate action? Political polarization creates significant challenges in achieving bipartisan support for climate legislation. Diverging views on climate change can stall critical policy initiatives and complicate negotiations.
What are some upcoming trends in climate legislation? Anticipated trends include increased focus on renewable energy investments, innovative technology solutions, and a growing acknowledgment of the interconnections between climate change and social justice.