Climate change, an intricate and interconnected global phenomenon, is n urbent issue that demands our attention. This post is meant to educate anyone unfamiliar with the causes, effects, or potential solutions to the complex challenge of climate change.
It’s no longer something we can choose to ignore. Glaciers are melting, we are experiencing extreme weather events in the U.S. both at higher rates and of increased severity. Temperatures are warmer and remain warm long after they should have cooled. Southern states are experiencing snowstorms and unprecedented hurricanes.
The Basics of Climate Change
At its core, climate change refers to long-term alterations in temperature and weather patterns on Earth. While natural processes influence climate, human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes, have accelerated these changes over the past century.
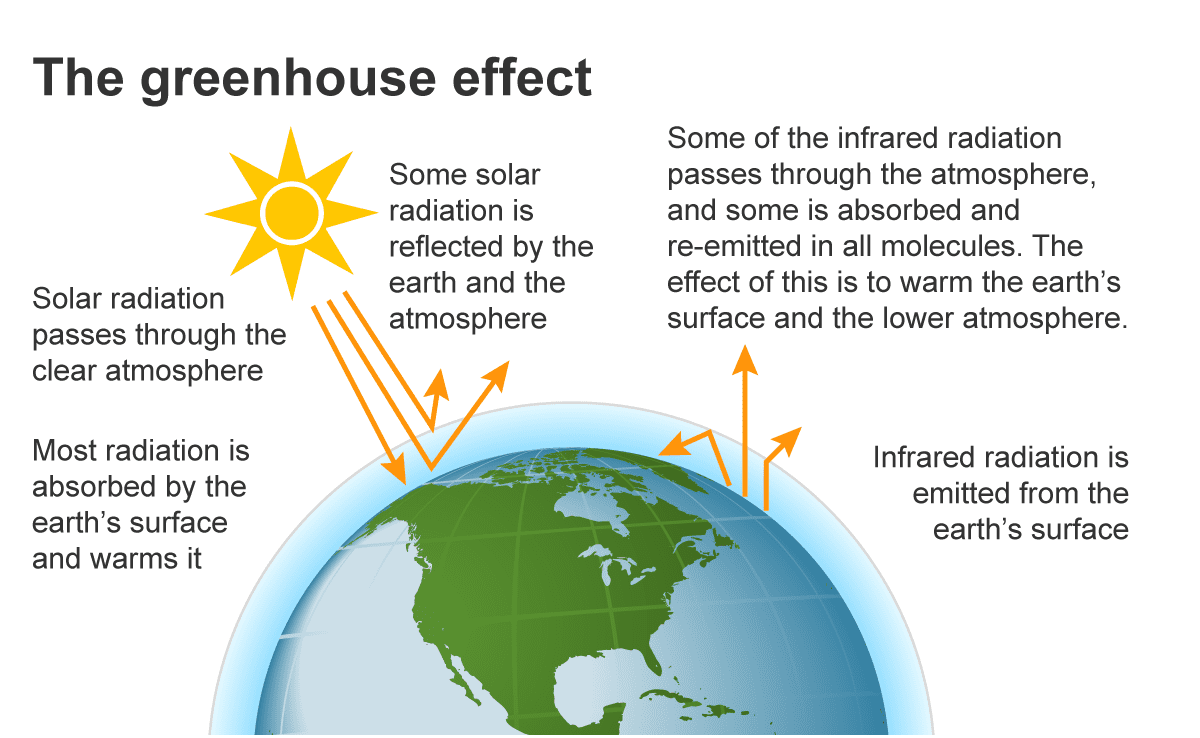
Greenhouse Gases and the Warming Effect
The primary driver of contemporary climate change is the increase in greenhouse gas concentrations, such as carbon dioxide (CO2) and methane (CH4). These gases trap heat in the Earth’s atmosphere, leading to a gradual warming known as the greenhouse effect.
Visible Consequences
Climate change manifests in various ways, impacting ecosystems, weather patterns, and sea levels. Some of the visible consequences include:
Rising Temperatures: Global temperatures are on the rise, resulting in heatwaves and altering natural temperature balances.
Extreme Weather Events: Increased frequency and intensity of events like hurricanes, floods, droughts, and wildfires are linked to climate change.
Melting Ice Caps and Rising Sea Levels: Warming temperatures contribute to the melting of glaciers and polar ice caps, causing sea levels to rise.
Ocean Acidification: Excess CO2 absorbed by oceans leads to increased acidity, posing threats to marine life.
Impact on Ecosystems and Biodiversity
Climate change poses significant threats to biodiversity, disrupting ecosystems and jeopardizing the survival of many plant and animal species. Shifts in temperature and precipitation patterns can affect migration patterns, reproduction, and the availability of food and habitats.
Mitigation and Adaptation
Mitigation: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions through renewable energy adoption, sustainable land use practices, and energy efficiency measures.
Adaptation: Preparing for and adapting to the changing climate by implementing resilient infrastructure, sustainable agriculture, and conservation efforts.

Global Cooperation
Given the transboundary nature of climate change, international collaboration is necessary. Agreements like the Paris Agreement, or Paris Climate Accords, aim to unite nations in collective efforts to limit global temperature increases and mitigate the impacts of climate change.
Climate change is an urgent global challenge that requires a collective response. Understanding its causes and consequences is the first step toward implementing effective mitigation and adaptation strategies. By embracing sustainable practices, advocating for policy changes, and fostering international cooperation, we can work towards a more resilient and sustainable future for our planet.
This requires Democratic politicians in the majority of both chambers of Congress and a President of the same party in office. Time and time again we see Democratic presidents come in and pass climate legislation to begin working to save the planet.
Next election cycle, a Republican president will come in and repeal all of the regulations and progress made by the previous administration. If we ever want to make real, impactful progress in addressing climate change, Americans will need to continue to elect Democratic presidents—at least until the Republican party changes it’s views on climate change and regulations on corporations and polluters that only damage the environment further.




